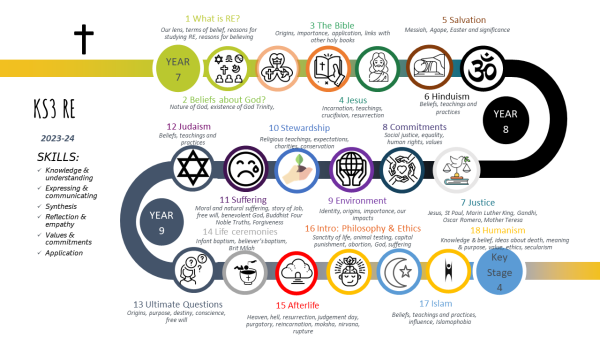
Faculty Introduction:
At KS4, Religious Education is delivered as a full GCSE in Philosophy and Ethics for six lessons a fortnight.
Philosophy and Ethics enables students to:
- Adopt an enquiring, critical and reflective approach to the study of religion
- Explore religions and beliefs, reflect on fundamental questions, engage with them intellectually and respond personally
- Enhance their spiritual and moral development, and contribute to their health and well being
- Enhance their personal, social and cultural development, their understanding of different cultures locally, nationally and in the wider world and to contribute to social and community cohesion
- Develop their interest in and enthusiasm for the study of religion, and relate it to the wider world
- Reflect on and develop their own values, opinions and attitudes in light of their learning.
- Gain an understanding of the beliefs of Christianity and how they impact on cultural and social issues in the community and family.
Topics / Modules to be covered:
Year 10 full course students will study four units as follows:
- Religion, crime and punishment
- Reasons for crime
- Attitudes to lawbreakers and different types of crime
- Aims of punishment
- Religious attitudes to suffering and the causes of suffering
- Treatment of criminals
- Religious attitudes to forgiveness
- Religious attitudes to the death penalty
- Relationships and families
- Human sexuality
- Marriage
- Divorce
- The nature and purpose of families
- Religious attitudes to gender equality
- Religion and Life
- The origins of the universe
- The value of the world
- Use and abuse of the environment
- Use and abuse of animals
- Abortion
- Euthanasia
- Death and the afterlife
- Religion, peace and conflict
- Violence
- Reasons for war
- Nuclear weapons
- The just war
- Holy war and religion as a cause of violence
- Pacifism and peacemaking
- Religious responses to victims of war
Year 10 short course students will study two units as follows:
- Relationships and Families
- This includes a selection of the topics from the same unit above
- Religion, peace and conflict
- This includes a selection of the topics from the same unit above
Year 11 full course students will study four units as follows:
Christianity: Beliefs and teachings
- The Nature of God
- The Trinity
- Biblical Creation
- The Problem of Evil
- Jesus Christ
- The Incarnation, Crucifixion, Resurrection and Ascension
- Salvation
Practices in Christianity
- Worship
- Sacraments
- Prayer
- Pilgrimage and Celebrations
- The Church in the Community
- Mission
- The Church in the World
Beliefs and Teachings of Islam
- Core Beliefs
- Nature of Allah
- Prophethood
- Books
- Angels
- Life After Death
- Practices in Islam
Importance of Practices
- Public Worship
- Private Worship
- Hajj
- Zakah
- Sawm
- Festivals
- Jihad
Year 11 2024 only:
This year, the Year 11s are studying a school-designed Introduction to Philosophy and Ethics unit, as we do not have enough time to deliver the GCSE Short Course unit. This Introduction to Philosophy and Ethics course explores philosophy and ethics by addressing fundamental questions and concepts. It examines the meaning of philosophy, the influence of Greek philosophers, the transmission of Greek thought through Islamic scholarship to Europe, and key philosophical questions, such as why there is something rather than nothing. Topics include Cosmological and Design arguments, the Big Bang Theory, evolution, and religious perspectives on these issues. Ethical dilemmas are discussed through theories like Utilitarianism, Situation Ethics, and Virtue Ethics, applying them to topics like abortion and euthanasia. The course emphasises key terms, extended answers, oracy, evaluative skills, and preparation for assessments.
Year 11 short course students will study two units as follows:
- Christianity: Beliefs and practices
- This includes a selection of the topics from the same units above
- Islam: Beliefs and practices
- This includes a selection of the topics from the same units above
Assessment:
GCSE Religious Education Key Exam Information Year 10
| Subject: Religious Studies |
|
| Exam Board |
AQA |
| Examination Details |
Paper 1 – 50% (96 marks)
Paper 2 – 50% (96 marks)
|
| Controlled Assessment |
None |
| Exam Paper Details |
Paper 1 – Christianity and Islam – Written Exam (1 hour 45 minutes)
Paper 2 – Thematic Studies – Written Exam (1 hour 45 minutes)
|
| Key Topics |
Component 1: The study of Christianity and Islam: beliefs, teachings and practices.
Component 2: Thematic studies. The choice of 4 philosophical and ethical themes out of 6.
A. Relationship and families
B. Religion and life
D. Peace and conflict
E. Crime and Punishment
|
GCSE Religious Education Key Exam Information Year 11
| Subject: Religious Studies |
|
| Exam Board |
OCR |
| Examination Details |
Paper 1 – 25% (63 marks)
Paper 2 – 25% (63 marks)
Paper 3 – 50% (126 marks)
|
| Controlled Assessment |
None |
| Exam Paper Details |
Paper 1 – All 4 topics examined in 1 hour and 45 minutes
|
| Key Topics |
Christian Beliefs, Teachings and Practices
Islamic Beliefs, Teachings and Practices
Relationships and families
The existence of God
Religion, peace and conflict
Dialogue between religious and non-religious beliefs and attitudes
|
Religious Studies and careers
The study of religions, philosophy and ethics develops key skills required in higher education and a broad range of careers. In fact, Philosophy forms one of the most popular courses at Oxford and Cambridge - PPE (Philosophy, Politics and Economics). The GCSE course ensures students adopt an enquiring, critical and reflective approach to fundamental questions. Students will learn to articulate their own beliefs as well as respecting those of others. Students will cultivate the compassion and empathy needed for careers in medicine, the tolerance and understanding essential for roles in policing and the analytical skills desired in law. Religious Studies closes no doors in careers, it only opens them.
Useful Websites (RE)